You’ve probably noticed how voice assistants have changed the way we interact with technology, but imagine taking that control to the next level with your own custom Arduino voice controller. Instead of relying on commercial devices with their limitations, you can build a system that responds exactly how you want it to. Your entertainment setup doesn’t have to be confined to manufacturer restrictions when you understand what’s truly possible.
Understanding Voice Recognition Technology for Entertainment Systems
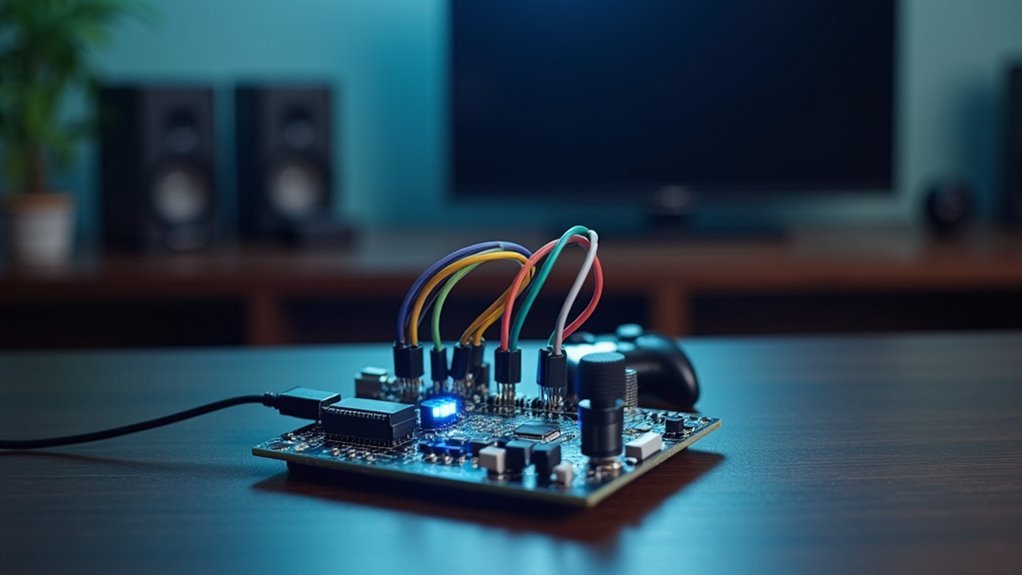
When you speak to your entertainment system, voice recognition technology transforms your words into digital commands that control everything from volume levels to content selection. This hands-free approach eliminates your dependency on physical remotes, letting you operate TVs, sound systems, and streaming services through simple verbal instructions.
Advanced speech recognition systems can identify different household members, automatically applying personalized settings and preferences. You’ll find voice control particularly valuable for complex tasks like searching specific content or managing multiple entertainment options.
Machine learning algorithms continuously improve accuracy by adapting to your unique speech patterns over time. Smart home integration creates cohesive environments where your voice-activated entertainment systems communicate with other IoT devices, enhancing accessibility and user experience throughout your connected home.
Essential Components for Building Arduino Voice Controllers
Building your own Arduino voice controller requires specific hardware components that work together to capture, process, and execute voice commands.
You’ll need an Arduino board like the Nano or Portenta H7 as your primary microcontroller for processing. A speech recognition module such as the Elechouse V3 or Grove Speech Recognizer handles voice recognition, storing multiple commands for entertainment applications.
The HC-05 bluetooth module enables wireless communication between your Arduino and mobile device, letting you send voice commands using your phone. An IR receiver and LED capture and replicate signals from existing remotes, allowing control over various entertainment devices.
Finally, jumper wires and a breadboard guarantee stable connections between all components, creating an organized voice controller system.
Setting Up IR Code Retrieval for Television Control

You’ll need to connect an IR receiver to your Arduino using jumper wires to capture the remote control signals from your existing TV remote.
Once connected, upload the IR_Read code and use the serial terminal to document the captured IR codes that correspond to each button press.
After gathering these codes, you’ll create a custom Arduino library with functions that replace generic commands with your documented IR codes for seamless television control.
Arduino IR Sensor Connections
Before you can control your television through voice commands, you’ll need to establish a reliable connection between an IR receiver and your Arduino to capture the remote’s infrared signals.
Connect the IR receiver’s output pin directly to any digital input pin on your Arduino board. The receiver requires a 5V power supply, so connect it to the Arduino’s 5V pin along with proper ground connections.
Upload the IR_Read code to your Arduino, then press various buttons on your TV remote. The captured IR codes will display in the serial terminal using pulseIR command format.
Document these codes as you’ll use them to create an Arduino library that emulates your remote’s commands, enabling seamless voice control integration for your entertainment system.
Capturing Remote Control Signals
Once your IR receiver connects properly to the Arduino, capturing your television’s remote control signals becomes a straightforward process that forms the foundation of your voice control system.
You’ll need to upload the IR_Read code to retrieve signals from your existing remote control for proper recognition.
Follow these essential steps:
- Document IR codes – Use the serial terminal to record the specific codes generated when you press each button on your remote control.
- Analyze pulseIR output – The retrieval process produces pulseIR commands that represent your remote’s various button functions.
- Create custom library – Build an Arduino library incorporating the documented IR codes, replacing function guts with your captured signals.
Save library files properly within the Arduino IDE to guarantee seamless recognition and television control integration.
Creating Custom Command Libraries
After capturing your remote’s IR signals, transforming raw pulseIR data into a functional command library requires organizing the documented codes into reusable Arduino functions. You’ll create a custom Arduino Library that replaces generic function templates with your specific IR codes captured from the serial terminal.
| Function Name | Remote Button | IR Code Example | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| powerToggle() | Power | 0xFF02FD | TV On/Off |
| volumeUp() | Vol+ | 0xFF40BF | Increase Volume |
| channelNext() | CH+ | 0xFF18E7 | Next Channel |
| muteAudio() | Mute | 0xFF52AD | Toggle Sound |
Save your library files correctly in the Arduino IDE’s library folder. This setup enables your voice controller to emulate remote functionality, sending direct commands to your television through organized, accessible functions.
Creating Custom Arduino Libraries for Remote Functions

You’ll streamline your Arduino voice controller project by organizing your captured IR codes into a custom library with proper structure and clear function names.
Start by creating a new folder in your Arduino libraries directory and establish the basic .h and .cpp files that’ll house your remote control functions.
This library structure lets you integrate all your television’s IR codes into reusable functions, making your entertainment system code cleaner and more maintainable.
Library Structure Setup
While setting up a custom Arduino library for remote functions might seem intimidating, the process becomes straightforward when you understand the essential file structure and organization requirements. The Arduino IDE recognizes libraries only when they’re properly organized in designated folders, making this setup vital for successful compilation.
Your library structure should follow these key components:
- Header file (.h) – Contains function declarations and necessary includes for IR communication protocols.
- Implementation file (.cpp) – Houses the actual code that controls your IR LED and sends pulseIR signals.
- Keywords file – Defines syntax highlighting for your custom functions within the IDE.
You’ll encapsulate the IR transmission code within these organized files, allowing you to replace internal functions with your recorded remote codes for seamless device customization.
IR Code Integration
Once you’ve established your library framework, capturing and integrating the actual IR codes becomes your next priority.
You’ll need an IR receiver connected to your Arduino to capture codes from your standard remote control. Open the serial terminal and press each button you want to replicate, documenting the unique hexadecimal values that appear. These IR codes form the foundation of your custom functions.
Next, create specific functions within your library that control the IR LED, allowing your Arduino to emulate those exact button presses. Reference Adafruit tutorials for proper implementation techniques and timing protocols.
Structure your library files correctly so the Arduino IDE recognizes them automatically. This integration transforms your voice controller into a powerful hub that can seamlessly operate multiple remote-controlled entertainment devices through simple voice commands.
Developing Voice-Activated Music System Controls
When developing voice-activated music system controls with Arduino, you’ll create an intuitive interface that transforms how you interact with your audio entertainment.
By integrating a speech recognition module with your Arduino board, you’ll program specific voice commands to execute various actions like play, pause, next track, and volume adjustment.
Program your Arduino to recognize voice commands for seamless music control including play, pause, track selection, and volume adjustment.
Your system’s core components include:
- Bluetooth connectivity for seamless streaming from Spotify or Apple Music through your smartphone
- LED feedback indicators that confirm command recognition and execution
- Customizable voice commands tailored to your personal preferences
This hands-free approach proves especially valuable for individuals with mobility challenges, eliminating the need for traditional remote controls.
You’ll enjoy enhanced accessibility while maintaining complete control over your music experience through simple voice interactions.
Integrating Bluetooth Communication for Wireless Commands
By incorporating Bluetooth communication into your Arduino voice controller, you’ll eliminate the constraints of wired connections and create a truly wireless entertainment command system. The HC-05 module enables seamless connectivity between your Android device and Arduino, transforming voice commands into actionable entertainment controls.
Your setup requires connecting the HC-05 to Arduino with proper voltage dividers to maintain 3.3V compatibility. Voice recognition apps like AMR_Voice convert spoken commands into string data that Arduino processes for specific actions.
| Component | Voltage | Function | Connection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arduino | 5V | Main Controller | Digital Pins |
| HC-05 | 3.3V | Bluetooth Module | UART Communication |
| Voltage Divider | 3.3V | Level Shifter | Between Modules |
| Android Device | Variable | Voice Input | Wireless Pairing |
This wireless approach enhances accessibility, allowing hands-free operation from any distance within Bluetooth range.
Programming Speech Recognition Modules for Entertainment Devices
When you’re selecting a speech recognition module for your entertainment setup, you’ll want to prioritize factors like recognition accuracy, command capacity, and compatibility with your Arduino board.
The Elechouse Voice Recognition Module V3 stands out because it can store up to 80 voice commands and doesn’t require an internet connection to function.
Once you’ve chosen your module, you’ll need to configure custom commands that match your specific entertainment devices, whether that’s “turn on TV,” “volume up,” or more complex sequences like “switch to Netflix and set volume to 20.”
Module Selection Criteria
Although numerous speech recognition modules exist for Arduino projects, you’ll need to evaluate several critical factors to choose the right one for your entertainment device.
These module selection criteria will determine your project’s success and user satisfaction.
First, verify compatibility with your Arduino board to guarantee seamless integration. Next, assess command storage capacity—higher capacity enables more complex voice interactions that’ll enhance your entertainment experience.
You’ll also want modules with excellent sensitivity and noise handling capabilities, since entertainment environments often have background audio.
Consider these essential features:
- Customizable wake words and commands for personalized user interactions
- Robust library support with thorough documentation
- Active community forums for troubleshooting assistance
These criteria guarantee you’ll select a module that delivers reliable voice control functionality.
Command Configuration Methods
Once you’ve selected the appropriate speech recognition module, you’ll need to configure specific voice commands that control your entertainment device’s core functions.
Using Arduino IDE, you can write custom code that integrates speech recognition capabilities through specialized libraries designed for modules like Elechouse or Grove. These command configuration methods allow you to program 5-20 specific voice commands tailored to your preferences, controlling volume adjustment, channel switching, and media playback functions.
You’ll create seamless interaction between voice commands and your entertainment devices while enhancing accessibility for users with disabilities.
Through testing and fine-tuning your setup, you can improve accuracy and responsiveness with real-time adjustments based on user feedback and environmental noise conditions, ensuring peak performance.
Building Voice-Controlled Lighting for Home Theaters
As you settle into your favorite recliner for movie night, fumbling for light switches in the dark becomes a thing of the past with Arduino-powered voice-controlled lighting systems.
Transform your movie nights with Arduino-powered voice control that eliminates fumbling for light switches in the dark.
You can create an immersive entertainment environment by integrating voice recognition modules like the Elechouse Voice Recognition Module V3 with your existing smart lighting setup.
The basic setup involves three essential components:
- Arduino board connected to relay modules controlling smart LED power
- Voice recognition modules programmed with custom commands like “dim the lights” or “turn on the projector”
- Smart home ecosystem integration for compatibility with Amazon Echo or Google Home
You’ll program specific lighting scenes tailored for different activities, whether you’re watching movies or gaming.
This voice-activated system enhances convenience and accessibility while maintaining your viewing experience.
Configuring Multiple Device Control Through Single Commands
You’ll need to establish a unified command architecture that connects your Arduino to multiple entertainment devices through a single voice interface.
This system requires configuring device synchronization methods that guarantee your TV, sound system, and other components respond simultaneously to commands like “Movie Time.”
Your Arduino can achieve this coordination by combining IR LED emitters, Bluetooth modules, and IoT relays to create seamless multi-device control.
Unified Command Architecture
When you’re tired of juggling multiple remotes and maneuvering complex device interfaces, Unified Command Architecture (UCA) transforms your Arduino voice controller into a centralized hub that manages your entire entertainment ecosystem through single spoken commands.
By integrating voice recognition modules like Elechouse or Grove with your Arduino system, you’ll program specific phrases that trigger coordinated actions across multiple devices simultaneously.
UCA works through three essential communication protocols:
- IR signals for traditional TVs and older equipment
- Bluetooth connectivity for wireless audio systems and modern devices
- Wi-Fi integration for smart streaming devices and network-connected equipment
Arduino’s flexibility lets you create custom libraries tailored to your specific devices, enabling personalized command sets that reflect your preferences.
You’ll initiate complex sequences—like powering on your TV while adjusting sound system volume—with a single voice command.
Device Synchronization Methods
While single device control provides basic functionality, synchronized multi-device operation creates truly seamless entertainment experiences where your Arduino voice controller orchestrates entire system responses.
You can implement device synchronization through Bluetooth modules like HC-05, enabling multiple devices to respond simultaneously to single voice commands.
IR LED and receiver setups allow you to program various entertainment devices for unified command recognition. Speech recognition modules such as Elechouse or Grove Speech Recognizer interpret voice inputs that trigger coordinated actions across your entire network.
The Software Serial library manages communication between your Arduino and multiple devices effectively.
You’ll achieve precise control by implementing relay systems that activate or deactivate different entertainment components through voice commands while maintaining perfect synchronization across all connected devices.
Implementing Smart Speaker Functionality With Arduino
Since Arduino microcontrollers offer impressive flexibility for custom electronics projects, you can transform them into sophisticated smart speakers that rival commercial alternatives.
By integrating voice recognition modules with speech recognition capabilities, you’ll create hands-free control systems for your entire entertainment setup.
Using Bluetooth modules like HC-05, you can establish wireless connections between your mobile device and entertainment systems.
Here’s what you can accomplish:
- Playlist Management – Control music playback, skip tracks, and organize audio content through vocal commands
- Volume Control – Adjust audio levels across multiple devices without touching physical controls
- Input Switching – Seamlessly change between different entertainment sources like streaming services or gaming consoles
You’ll customize voice commands to recognize specific phrases that match your preferences, creating a personalized entertainment interface that integrates seamlessly with IoT-enabled smart home devices.
Designing Voice-Activated Gaming Console Controllers
Beyond smart speakers, voice technology opens up exciting possibilities for gaming applications. You’ll find that Arduino-based voice-activated gaming controllers revolutionize how you interact with games, offering hands-free gameplay through speech recognition technology.
Using an Arduino microcontroller with modules like the Elechouse Voice Recognition Module, you can create controllers that respond to specific voice commands. Simply connect the components with jumper wires and program voice patterns for actions like jumping or menu navigation.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Arduino Microcontroller | Processes voice commands |
| Speech Recognition Module | Captures and interprets audio |
| Bluetooth Module | Wireless console communication |
| Jumper Wires | Component connections |
| Power Supply | System operation |
These customizable controllers support multiple gaming platforms while enhancing accessibility for players with disabilities, creating inclusive gaming experiences that align with industry innovation trends.
Troubleshooting Common Voice Recognition Issues
Although Arduino voice controllers offer exciting gaming possibilities, you’ll inevitably encounter recognition issues that can disrupt your gameplay experience. When your commands aren’t registering properly, don’t panic—most problems have straightforward solutions.
Start by addressing these fundamental issues:
When voice commands fail during gameplay, tackle the basics first before diving into complex troubleshooting procedures.
- Position your microphone correctly and remove any obstructions that might interfere with sound capture or introduce background noise.
- Verify your serial communication settings match the required baud rate and configurations for seamless Arduino-to-module communication.
- Test commands in quiet environments first, since competing sounds can cause misinterpretation or complete recognition failure.
If problems persist, retrain your speech recognition module with clearer pronunciations and command variations.
Additionally, keep your firmware and Arduino libraries updated to access the latest recognition algorithm improvements.
Expanding Systems for Multi-Room Entertainment Control
Once you’ve mastered voice control for a single gaming setup, you can expand your Arduino system to manage entertainment across multiple rooms in your home.
Start by integrating HC-05 Bluetooth modules to connect with smartphones and tablets, enabling wireless voice commands from anywhere. You’ll be able to control multi-room audio systems, adjusting playback and volume across different zones through simple voice phrases.
Program voice recognition modules to respond to personalized commands for lighting and AV equipment in each room.
Install IoT relays to power entertainment devices like TVs and speakers on or off simultaneously. By implementing speech recognition technology into your existing home network, you’ll create seamless integration with smart home devices, establishing a cohesive multi-room entertainment environment that responds to your voice commands.
Advanced Customization Options for Entertainment Automation
When you’re ready to take entertainment automation beyond basic commands, Arduino voice controllers offer extensive customization options that transform your entire home theater experience.
You can program complex multi-command sequences that execute multiple actions simultaneously, creating seamless entertainment scenarios.
Here are three advanced customization options you can implement:
Three powerful Arduino customization techniques can elevate your voice-controlled entertainment system from simple commands to sophisticated automated experiences.
- Custom IR Libraries – Write personalized code using Arduino IDE to emulate any remote control, enabling voice commands to replace traditional remotes entirely.
- Multi-Command Sequences – Program complex actions like “movie night” that automatically dims lights, powers on your TV, and starts your preferred streaming service.
- Wireless Integration – Utilize Bluetooth modules for smartphone connectivity, allowing voice commands to be transmitted wirelessly across your entertainment system for enhanced flexibility and control.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Arduino Do Voice Recognition?
You can implement voice recognition with Arduino using dedicated modules like Elechouse Voice Recognition Module V3 or Grove Speech Recognizer. You’ll process commands locally without internet, enabling custom voice-controlled projects for automation and robotics.
What Is the Voice Detection Module for Arduino?
You’ll use modules like the Elechouse Voice Recognition Module V3, which features built-in microphones and supports customizable trigger phrases. These modules require minimal setup and let you train them to recognize specific voice commands easily.
How Can Arduino Be Used to Build a Home Automation System With Voice Control or Smartphone Integration?
You’ll connect voice recognition modules like Elechouse or HC-05 Bluetooth to Arduino, then program it to control IoT relays that switch lights, fans, and appliances through smartphone apps or spoken commands safely.
How to Make a Voice-Controlled Robot?
You’ll connect an HC-05 Bluetooth module and speech recognition module to your Arduino, then program it to interpret voice commands from an Android app for controlling robot movements like forward, backward, and turning.





Leave a Reply